The word fistula comes from a Latin word meaning pipe or tube. Medically, a fistula refers to an abnormal connection that forms a canal between two hollow spaces. This can be intestines, blood vessels or other hollow organs. The term ‘hollow organs’ refers to visceral organs that consists of a hollow tube, such as your stomach, or that include a cavity, like your bladder or heart. Fistulas are often caused by surgery or an injury, but they can also form in response to inflammation or an infection.
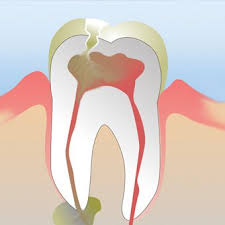
In this article, we are going to discuss one of the more common fistulas that occurs, which results from a tooth that has become so infected that a pus-filled canal forms along your sinus tract, causing a boil to form on your gums. If left untreated, an abscess on your tooth can become so large that it permeates the bones in your mouth, extending into the soft tissue and eventually developing into both Osteomyelitis (an inflammation of your bones that requires surgery in order to remove the dead areas of your bone) and Cellulitis (a common, yet potentially severe bacterial infection of the skin).
Once your bone begins to die and your gums become infected, a pathway develops that results in the fistula spreading even further, either externally or internally. Drainage often starts as a boil that forms on your gum as the result of inflammation and swelling of the gums surrounding the infected tooth. Eventually the boil bursts, resulting in the drainage of the pus from your abscessed tooth within your mouth, seeping out of the pus-filled fistula canal. Usually, after the boil pops, the pus drainage will relieve the mass, thus reducing the symptom of painful pressure that has been building up. However, this is not always the case. Depending on how serious the infection is, some people might feel slightly sick, while others develop severe symptoms that require hospitalisation. One reason why a fistula gum boil is painless is because, instead of sore busting from intense pressure, instead the pus slowly seeps out of the boil. While suffering from an abscessed tooth and the resulting fistula doesn’t sound pleasant, it does alert you to the fact that something is wrong, prompting a visit to your dentist early enough that it can be treated before it becomes more serious.
There are multiple complications associated with a fistula gum sores. Even if the fistula gum boil isn’t painful doesn’t mean that you don’t require treatment. If your abscessed tooth go untreated, severe complications can develop, which can drastically affect your health and may even be fatal in extreme cases. Should you be able to feel and notice the appearance of a boil on your gums, you should see your dentist immediately, even if you aren’t experiencing any pain.
Abscesses will not go away on their own and require prompt and proper dental treatment. If an abscessed tooth is treated properly, your dentist should be about to save your tooth and eliminate the infection, preventing complications. In most cases, treating the tooth will first require a draining of the abscess. The best way to drain the infected tooth is by performing a root canal. Should the infection be treated, yet a diseased root still remains, root surgery is the next step. After the abscess is drained and the infection gone, a crown is placed over your treated tooth.
If you believe you have an infected tooth, contact us to arrange an evaluation.